Since the inception of the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program (MDRP) in 1990, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has used its negotiating power to reduce costs for drugs prescribed to Medicaid and Medicare beneficiaries. If they meet the eligibility criteria, certain hospitals, clinics, drug assistance programs, and treatment centers – known as “covered entities” – gain access to these same discounted prices through the 340B Drug Pricing Program.
Within HHS, the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) and its Office of Pharmacy Affairs (OPA) are responsible for overseeing the program and conducting audits to ensure regulatory compliance among covered entities. With the right strategies and tools, covered entities can implement and improve procedures that successfully prepare them for 340B audits.
Maintaining 340B Compliance Is Critical
As of 2021, HHS has created pricing agreements with an estimated 780 drug manufacturers. Collectively, state Medicaid programs represent the largest share of prescription drug spending in the United States. From 2018 to 2020 alone, annual spending on Medicaid outpatient prescriptions rose from $16.5 billion to $19 billion.

Clearly, the pricing agreements established through the MDRP have far-reaching benefits, these significant discounts on prescription drugs can be a lifeline for providers serving low-income and vulnerable populations. Participation in the 340B Program often determines whether a healthcare facility can survive while serving vulnerable communities. To retain access to 340B pricing, covered entities need to stay in compliance with program requirements, including:
- Facility and pharmacy registration.
- Annual recertification of eligibility.
- Ensuring patient eligibility for discounted prescriptions.
- Accurate reporting on billing practices for discounted drugs.
- Auditable documentation of compliance protocols.
7 Steps to Follow When Preparing for a 340B Audit
When preparing for an audit from the HRSA, best practices for covered entities fall into two broad categories: long-term, ongoing efforts and pre-audit preparedness.
From a long-term view, covered entities should consistently:
1. Maintain compliance documentation.
Covered entities should always maintain documentation on key policies and procedures concerning compliance with program requirements.
2. Perform Internal audits.
By conducting thorough internal audits, healthcare organizations can often update their existing procedures and policies to address gaps in their compliance strategy. To be effective, internal auditing should occur regularly and should cover as many program requirements as possible. Additionally, HRSC auditors may want to know about internal auditing practices as part of an official audit.
In anticipation of an official audit (and as part of internal audits), covered entities should:
3. Check their registration in the OPA Information Service (OPAIS) database.
Each covered entity needs to ensure their registration is updated, has correct information, and includes primary and satellite facilities and pharmacies.
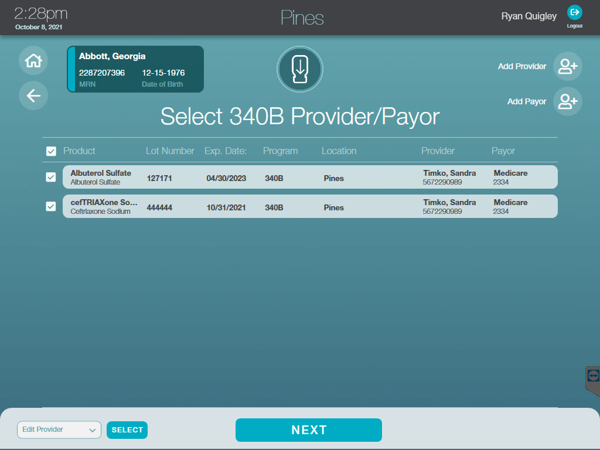
4. Test and confirm eligibility of previous transactions for mixed-use settings (providing both inpatient and outpatient services) and contract pharmacies.
To perform this test, internal auditors would need to select and examine a significant number of prescription orders fulfilled through the 340B Program and check if they were actually qualified. Auditors need to check their records to determine if a qualifying provider wrote the prescription and whether the medication was dispensed in an eligible facility for outpatient use.
5. Assess 340B compliance policies and procedures.
Among other compliance protocols, covered entities should have documented procedures for:
- Inventory management, accumulations, and reporting
- Eligibility determinations.
- Billing and reporting to Medicaid (preventing duplicate discounts).
- Oversight of contract pharmacies and satellite facilities
- Accumulation and medication procurement.
- Annual recertification.
6. Compare inventory and purchasing records for each facility and purchasing account.
7. Review the latest Medicaid cost report that the entity filed, looking for any discrepancies between total charges and Medicaid charges by cost center.
How Does a 340B Audit Work?
Before the audit process begins, the HRSA notifies covered entities’ that they have been selected for a 340B audit, typically with one or two weeks’ advance notice. Once an audit is scheduled, the HRSA requests records on 340B prescriptions, inventory, related purchases, participating facilities, eligible providers, Medicare cost reports, and compliance policies and procedures.
After the on-site audit, the HRSA issues a final report detailing their findings. The covered entity then has 30 days to submit any disagreements or 60 days to submit a Corrective Action Plan (CAP) – without this plan, the covered entity risks removal from the 340B Program.
Both the HRSA and 340B manufacturers can conduct these audits. However, manufacturers have considerably less authority in this area. For example, they can only assess compliance related to duplicate discounts (receiving discounted drug prices and manufacturer rebates) or the diversion of 340B drugs for resale or repurposing.
When raising these concerns, manufacturers are expected to inform covered entities first and coordinate with them to correct any problems. Even then, they can only conduct an audit once they “demonstrate [they have] reasonable cause.”

What Happens If a Covered Entity Is Not in Compliance?
Failure to comply with 340B Program requirements can cost healthcare organizations their enrollment in the 340B Program. Not only can program removal threaten healthcare organizations’ business viability, but it can also come with significant financial penalties. Non-compliant covered entities may have to reimburse pharmaceutical manufacturers for any rebates or discounts they’ve received.
Although both HHS and the HRSA have published documentation on how they review covered entities to ensure program integrity, understanding how to properly apply this information can be challenging, especially for large organizations. Participating healthcare facilities need to establish dedicated resources and long-term strategies to properly prepare them for 340B audits.
Stay Audit Ready with a Strong Compliance Program
As the HRSA describes it, the 340B Program allows “covered entities to stretch scarce federal resources [to reach] reaching more eligible patients and [provide] more comprehensive services.” The purpose of 340B audits isn’t necessarily to exclude or punish covered facilities but rather to ensure that the program’s essential purpose is protected.
By implementing a comprehensive compliance program, covered entities can remain prepared for an audit. To prepare your organization, your ongoing compliance program should include:
-
Appointing an internal review committee for 340B compliance.
-
Regular self-audits and reviews of your facilities’ policies and procedures.
-
Periodically using independent auditing services
-
Standard processes for updating policies and procedures when needed.
-
Checks in place to verify OPAIS database registration of your organization and all its facilities.
-
Processes and solutions in place that simplify inventory management and documentation.
A strong compliance program allows you to identify and address existing issues long before they result in audit failures or costly penalties.
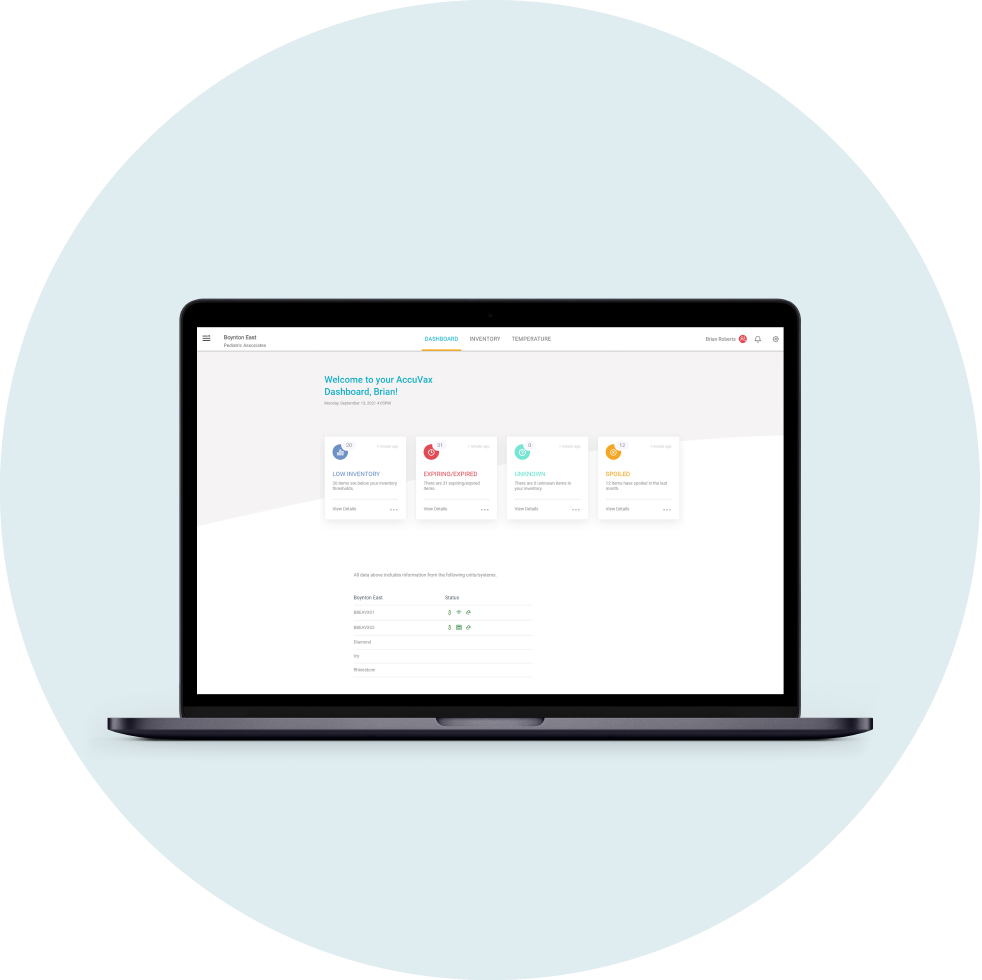
With manual records-keeping, your organization risks compromising your 340B compliance through human error and inconsistency. To simplify your 340B workflows and reduce the burden of labor-intensive inventory management on your staff, see how our AccuVax and AccuShelf systems can help you stay audit ready.
Stay Audit Ready
Save time and manual effort.
The hardest part of 340B compliance is the manual effort. Your practice needs to separate inventory and track every dose of medication by invoice, provider, and prescriber. Each of these tasks may only take a few minutes but they really start to add up at a busy practice, which means less time for staff to provide top of license care to their patients. At TruMed, we simplify the complex process of maintaining 340B program compliance resulting in critical 340B cost savings for our customers and time saved preparing for HRSA audits.
340B Support & Compliance
The AccuShelf and AccuVax offer a configurable option to automatically capture provider, payor, invoice, and transaction data for all of your 340B vaccines and medications. With built-in reporting, you can eliminate cumbersome manual compliance efforts and view, export, or print your up-to-date information whenever you need it, simplifying internal audits.
Centralized Reporting
Manages multiple accounts or departments with one secured cloud-based platform
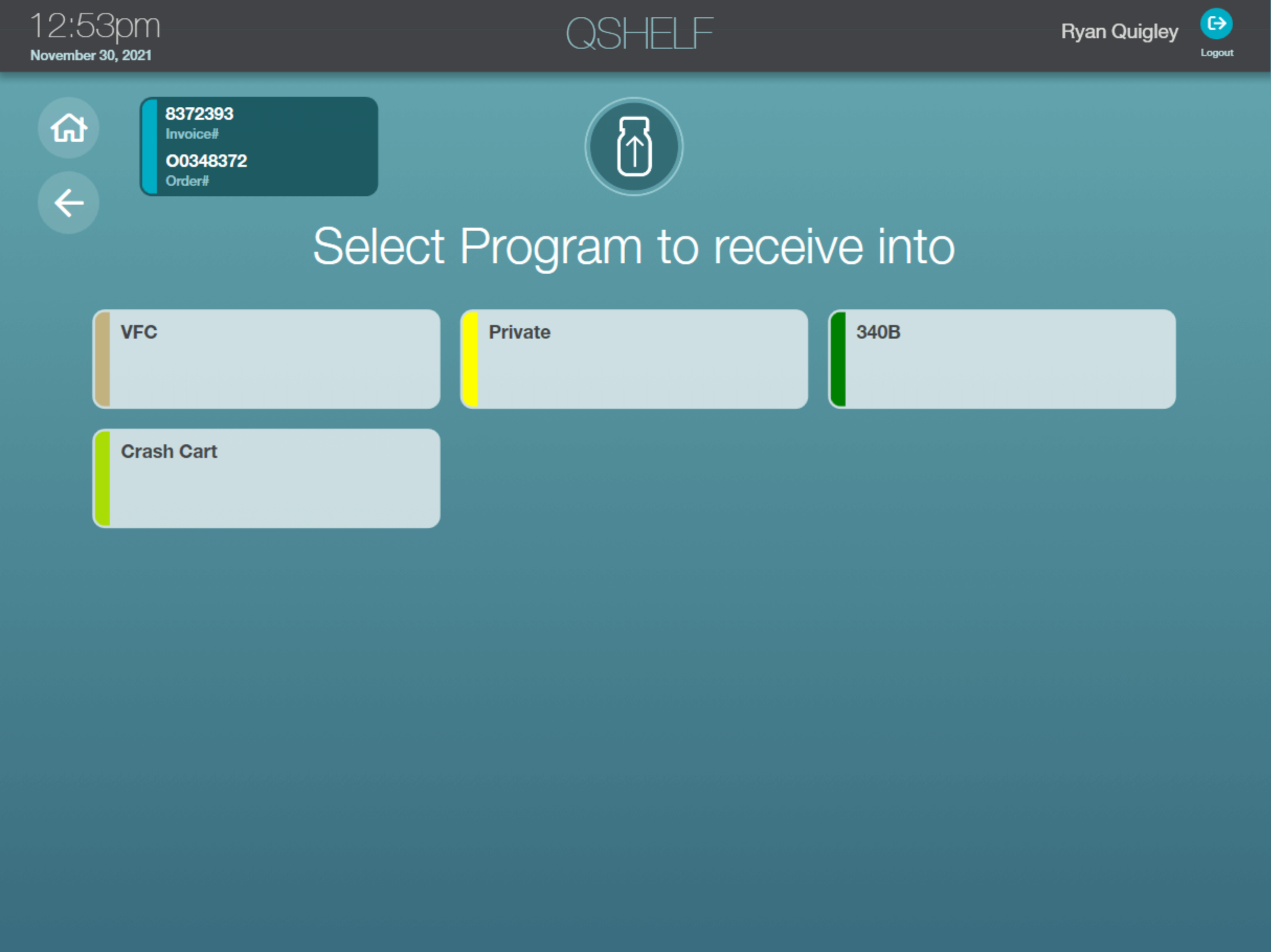
Simplify 340B Workflows
Support 340B workflows with inventory separation and dose tracking by invoice, provider and more
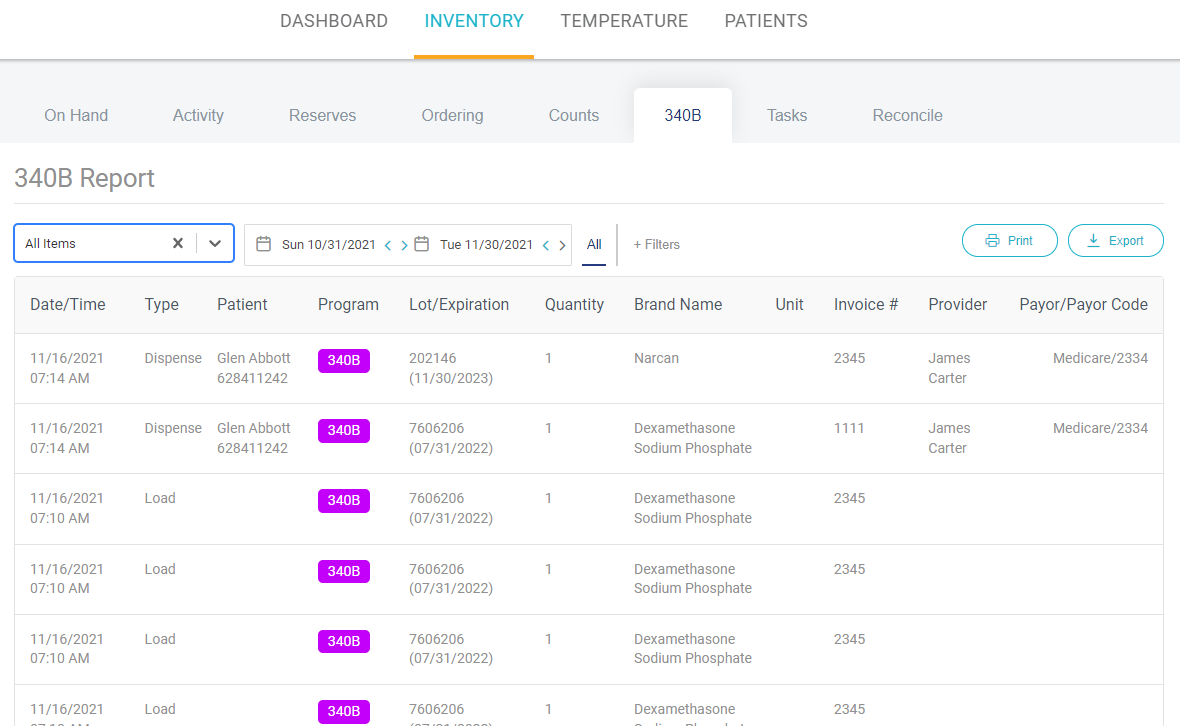
Stay Audit Ready
Generate required compliance and medication audit reports with verification of data for adherence to compliance standards